This comprehensive course of 15+ hours covers the fundamentals and advanced topics of Sheet Metal engineering & it focus more on costing of sheet metal component and assemblies.
This course is ideal for mechanical, aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing engineers, design engineers, fabrication specialists, and quality control professionals seeking to enhance their skills in sheet metal costing.
Direct costs-These are important to consider when setting product prices because they represent the minimum amount needed to break even on production.
Manufacturing overhead-Keeping track of manufacturing overhead costs can help you determine your business's performance and efficiency.
Direct labour-This is an important part of the total cost of producing a product. To calculate direct labour costs, you can track the time employees spend on different activities and multiply their pay rate by the amount of time they spent on a project.
Cost allocation
This involves tracking and aggregating business expenses to assign them to specific cost objects, such as a product's production.
Gross margin-This is a key business metric that indicates how well a business manages its costs. You can estimate your gross margin by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the total revenue.
Overhead costs-Accurately allocating overhead costs is important for effective product costing. This can help with making correct managerial decisions, such as pricing decisions.
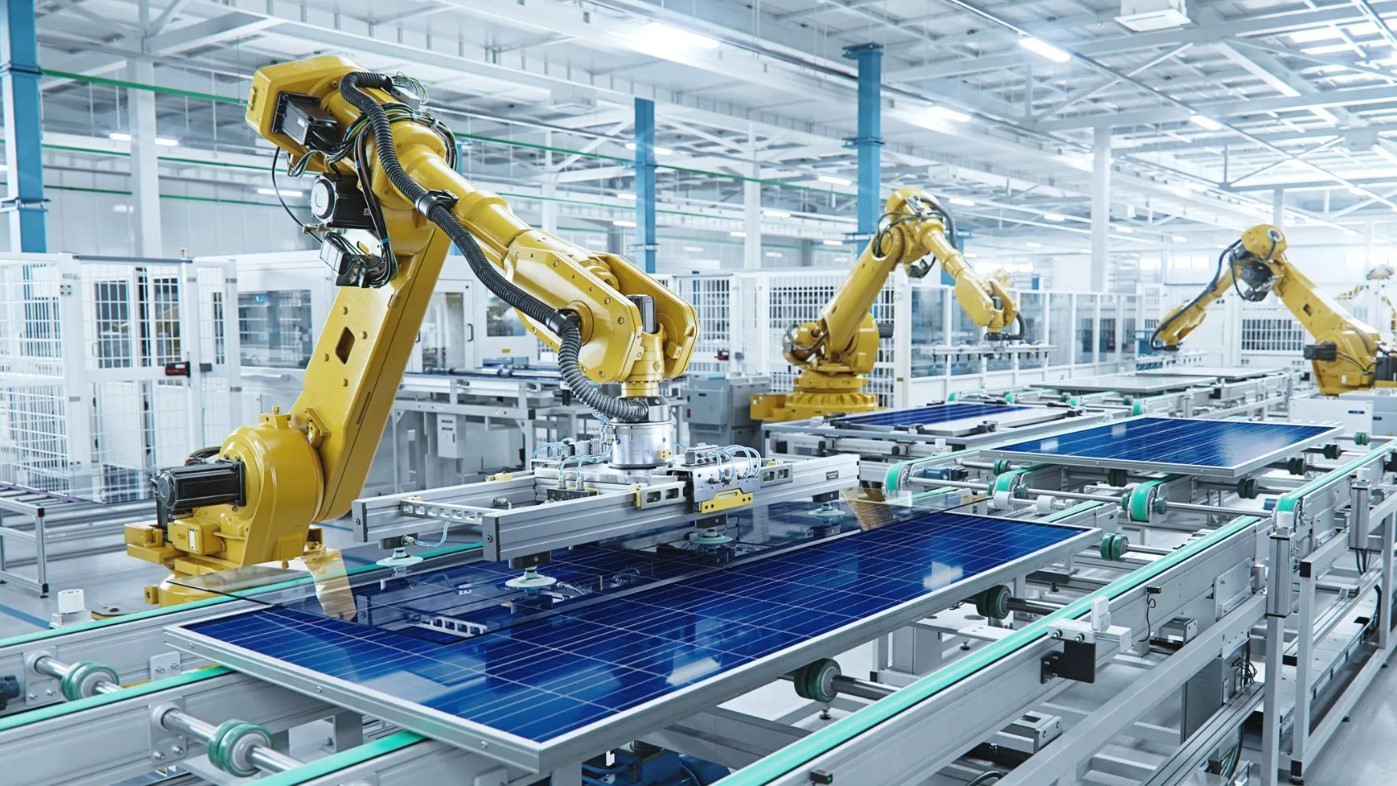
Sheet metal is metal formed into thin, flat pieces, usually by an industrial process. Sheet metal is used in automobile and truck (lorry) bodies, major appliances, airplane fuselages and wings, tinplate for tin cans, roofing for buildings (architecture), and many other applications. Sheet metal of iron and other materials with high magnetic permeability, also known as laminated steel cores, has applications in transformers and electric machines. Historically, an important use of sheet metal was in plate armor worn by cavalry, and sheet metal continues to have many decorative uses, including in horse tack.