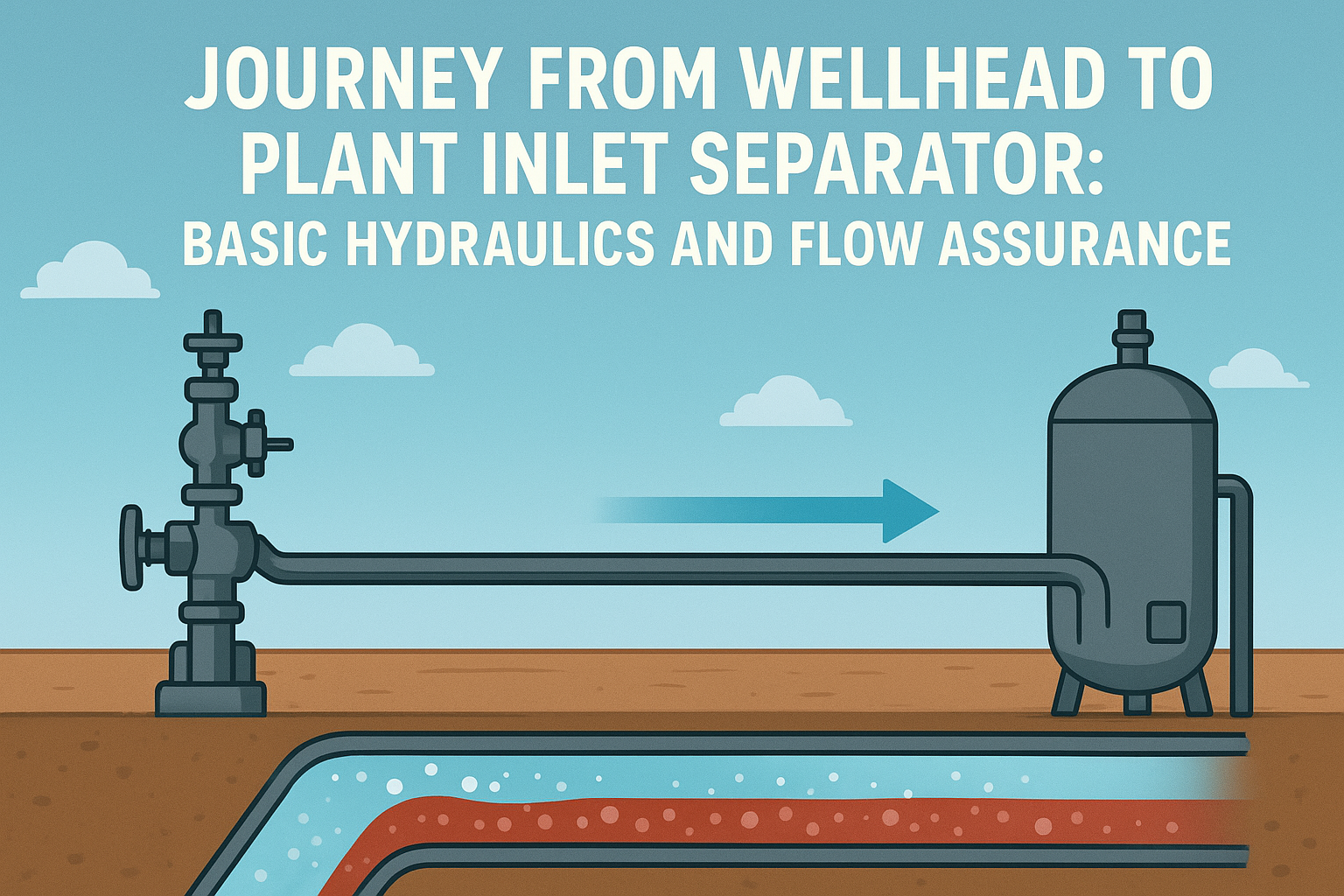
Isometric Projection: Isometric Drawings and Isometric Views

MANAS PATNAIK
Mechanical Engineer and Teacher
$ 21
Beginner course for learners

Isometric Projection: Isometric Drawings and Isometric Views
Trainers feedback
0
(0 reviews)
MANAS PATNAIK
Mechanical Engineer and Teacher
Course type
Watch to learn anytime
Course duration
120 Min
Course start date & time
Access anytime
Language
English
This course format through pre-recorded video. You can buy and watch it to learn at any time.
Why enroll
People enroll in this course to develop essential skills in creating and interpreting isometric drawings and views, which are crucial for fields like engineering, architecture, and product design. Whether they are beginners looking to grasp the basics or intermediate learners wanting to refine their techniques, this course provides the knowledge and practice needed to accurately represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional surface. By mastering isometric projection, students can improve their technical drawing abilities, spatial reasoning, and overall design proficiency.
Course content
The course is readily available, allowing learners to start and complete it at their own pace.
Isometric Projection: Isometric Drawings and Isometric Views
24 Lectures
120 min
Isometric Projection | Concept and Objective Problems
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 1
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 2
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 3
5 min
Learn to create isometric view of a circle
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 4
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 5
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 6
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 7
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 8
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 9
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 10
5 min
Isometric Views Problem 11
5 min
Isometric View_Pentagonal Pyramid
5 min
Isometric View_Pentagonal Prism
5 min
Isometric View_Cylinder & Cone
5 min
Isometric View_Frustum of Cone
5 min
Question
5 min
PYQ
5 min
PYQ
5 min
PYQ
5 min
PYQ
5 min
PYQ
5 min
PYQ
5 min
Course details
This course offers an in-depth exploration of isometric projection, a key technique in technical drawing and design. Students will learn to create and interpret isometric drawings and views, mastering the art of representing three-dimensional objects on two-dimensional surfaces. The course covers the fundamentals of isometric axes, angles, and scale, guiding learners through the process of sketching and visualizing objects in an isometric perspective.
Course suitable for
Automotive Mechanical
Key topics covered
Why people choose EveryEng
Industry-aligned courses, expert training, hands-on learning, recognized certifications, and job opportunities—all in a flexible and supportive environment.
- Industry Veteran
- Trainer Review

MANAS PATNAIK
Mechanical Engineer and Teacher
Questions and Answers
A: Certainly! Beginners can start with online tutorials and courses that introduce the basics of isometric drawing and projection. Websites like Khan Academy and YouTube have video tutorials demonstrating step-by-step methods. For example, the "Isometric Drawing Basics" video by 'Learn Engineering' on YouTube provides a clear explanation. Additionally, CAD software tutorials on platforms like Autodesk University and LinkedIn Learning offer practical training using digital tools. For textbooks, 'Engineering Drawing and Design' by David A. Madsen is a widely recommended resource. Always practice with isometric grid paper to build skill.
A: In isometric drawings, all three axes (X, Y, and Z) are equally scaled and drawn at 120 degrees from each other, which preserves the proportions of the object without perspective distortion. Because of this, distances measured along these axes reflect the object's true dimensions without the need for additional scaling or conversion. This makes isometric drawings particularly useful in technical contexts where precise measurements are vital. However, measurements along diagonal or curved lines in the isometric view may need careful interpretation.
A: While isometric projection provides a clear and undistorted representation of three-dimensional objects, it has limitations. One disadvantage is the inability to represent objects with complex curves or detailed shading realistically, as it lacks perspective depth. Additionally, the angles and foreshortening can sometimes make it difficult to interpret spatial relationships intuitively, especially for those unfamiliar with isometric views. Also, because all axes are equally foreshortened, the representation may appear less natural than perspective drawings. For some applications, other projections like perspective or orthographic might be more suitable.
A: Isometric projection is a type of axonometric projection where the scale along all three axes is equal, and the axes are separated by 120 degrees. Other axonometric projections include dimetric and trimetric projections, where scales along the axes differ, and the angles between axes are not equal. Dimetric projection uses two scales and two equal angles, while trimetric uses three different scales and angles. These variations can provide more realistic views but are more complex to construct. Isometric projection offers a balance of simplicity and clarity, which is why it's widely used.
A: Isometric drawings are used extensively in engineering, architecture, and product design to convey complex spatial relationships clearly. They are ideal for visualizing mechanical parts and assemblies without distortion, facilitating easier interpretation and communication among engineers, designers, and manufacturers. Applications include technical manuals, assembly instructions, piping and instrumentation diagrams, and architectural floor plans. Their uniform scale makes them useful for detailed dimensioning and part fabrication.
A: An isometric drawing is a type of pictorial drawing representing an object in three dimensions on a two-dimensional plane using isometric projection principles. It typically shows three faces of an object (front, top, and side) in a single view. An isometric view, on the other hand, refers to the perspective or angle at which the object is visualized or rendered following isometric projection rules. Essentially, the isometric drawing is the final illustration, while the isometric view describes the orientation used to create that illustration.
A: To create an isometric drawing manually, begin by drawing three axes originating from a single point: one vertical and two at 30 degrees to the horizontal on either side. Use these axes as guides for drawing the object's edges. Start by sketching the front, top, and side views scaled equally along these axes. Maintain equal measurements along the three axes since isometric projection does not distort size. Using an isometric grid paper can help maintain accuracy. This method allows for visualizing the object in three dimensions while preserving dimensional relationships.
A: Traditional tools for isometric drawings include isometric grid paper, a T-square, set squares (30/60 degree triangles), pencils, erasers, and rulers. For digital drawings, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or SketchUp are widely used, as they provide isometric view options and precision tools. These software solutions can generate accurate isometric views from 3D models and facilitate adjustments easily.
A: Isometric projection is a method of visually representing three-dimensional objects in two dimensions, where the three coordinate axes appear equally foreshortened and the angle between any two of them is 120 degrees. Unlike perspective projection, where objects appear smaller with distance, in isometric projection, the scale is uniform, allowing measurements to be taken directly from the drawing. It is commonly used in engineering and technical drawings due to its ability to represent complex objects clearly without distortion. For more details, you can refer to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isometric_projection.
A: An isometric grid is a network of lines arranged at 30-degree angles relative to the horizontal, producing a pattern of equilateral triangles. This grid provides a guideline for accurately positioning and scaling objects and edges along the three isometric axes. It helps artists and engineers maintain consistent angles and proportions when sketching or drafting isometric drawings by hand. Using an isometric grid reduces errors and accelerates the drawing process, especially for complex shapes. Many drawing software programs include an isometric grid option for the same purpose.
More from Same Author
- Technical Courses
- Articles
50
Online
Live courses
Beginner
Online
Live courses
Interacting with trainer
4
113
Online
Live courses
Intermediate
Online
Live courses
Interacting with trainer
4
503
3
E-Learning
Unlimited access
Beginner
E-Learning
Unlimited access
Pre-recorded videos
Earning and Growth option in same Industry Domain
- Pre-recorded
- Online live session
- Offline
- Articles
4
491
E-Learning
Unlimited access
Beginner
E-Learning
Unlimited access
Pre-recorded videos
4
467
E-Learning
Unlimited access
Beginner
E-Learning
Unlimited access
Pre-recorded videos
4
478
1
E-Learning
Unlimited access
Beginner
E-Learning
Unlimited access
Pre-recorded videos
More Training & Development option to expand your reach
- Technical courses
- Soft-skills courses
- Seminars
- Articles & Blogs
4
403
Online
Live courses
December 21
1.5 Hrs
Beginner
Online
Live courses
Interacting with trainer
998
3
Online
Live courses
December 31
160 Hrs
Advanced
Online
Live courses
Interacting with trainer
254
Online
Live courses
January 8
9 Hrs
Beginner
Online
Live courses
Interacting with trainer