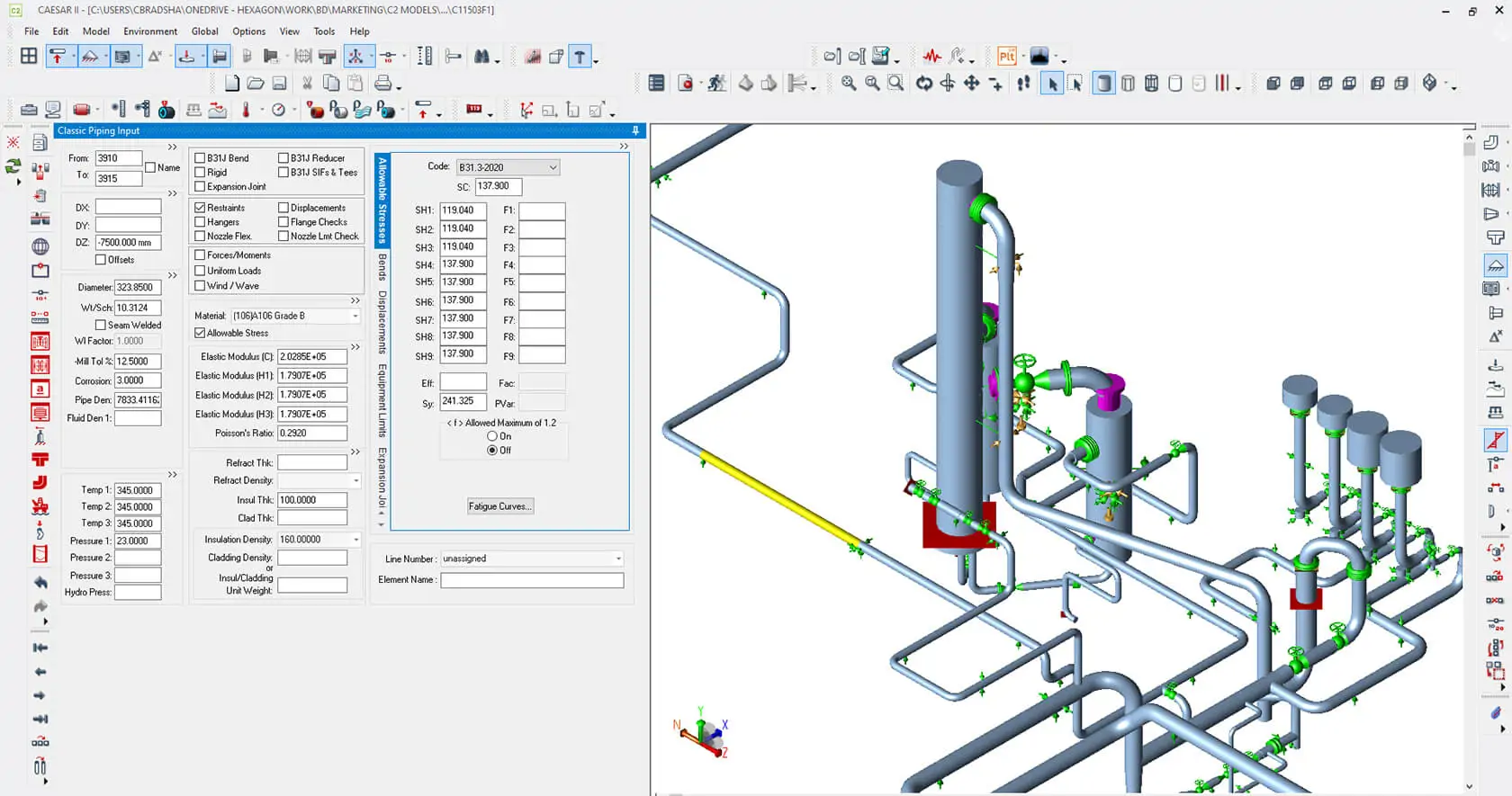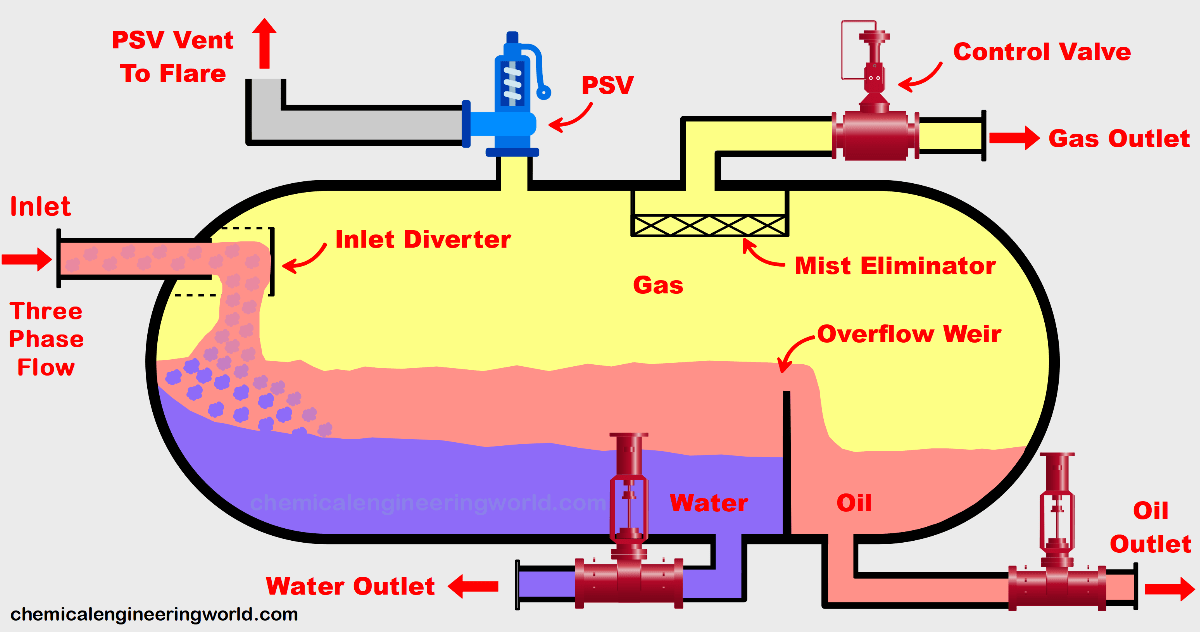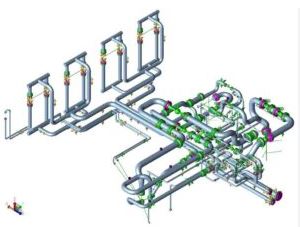
Preview this course
Advanced Pipe Stress Analysis Training with Caesar II | For Beginners & Engineering Professionals
$ 500
38 already enrolled!
Why enroll
Opportunities that awaits you!

Earn a course completion certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV. Share it on social media and in your performance review
Course content
The course is readily available, allowing learners to start and complete it at their own pace.
Course details
Course suitable for
Why people choose EveryEng
Industry-aligned courses, expert training, hands-on learning, recognized certifications, and job opportunities—all in a flexible and supportive environment.
- Industry Veteran
- Trainer Review
❮
❯